Auto tag EC2 instances using Amazon EventBridge and deploy Infrastructure with Github Actions
Use Case
Tagging AWS resources is very important when you want to automate some tasks based on the tags, like you want to install patch automatically based on the tags from SSM association or you want to get a list of resources based on
the tags. There are many aspects where tagging the resources will be required.
In this blog, I will be showing on automatically adding a tag to EC2 instances with platform OS version and Launched By details. This use case will be helpful when we want to target any API actions to multiple EC2 instances
of particular OS type. Example, if you have multiple different flavors of Operating systems in your Organization and you want to apply emergency patch to a windows instance and if you don't have the tags then grouping and
applying the patches would be tedious task. In this blog we will be focusing on the how to automatically tag an instances with OS tag. Let’s get started.
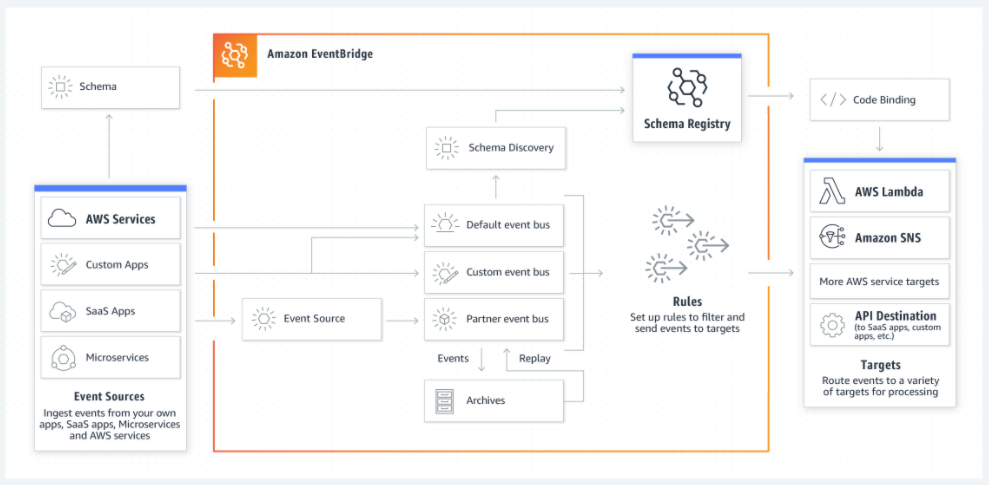
Amazon EventBridge
Amazon EventBridge is a serverless event bus service that makes it easy to connect your applications with data from a variety of sources. EventBridge delivers a stream of real-time data from your own applications, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) applications, and AWS services and routes that data to targets such as AWS Lambda. You can set up routing rules to determine where to send your data to build application architectures that react in real time to all of your data sources.Design Overview

Implementation
I have packaged all the above resources with Infrastructure as a code using CloudFormation to create AWS EventBridge, AWS Lambda and necessary IAM roles. Also in this blog, I will show you on how you can deploy this
package using Github Actions. Below is the deployment process for our implementation.
In the deployment package, as a pre-requisite, CloudTrail Trail should be created. For more details on creating the Trail, please refer
AWS official doc


I will walk you through the each steps on the implementation. Below is the high-level details on the IaaC and workflow:
- CloudFormation template will create below AWS resources:
- AWS EventBridge
- IAM Role
- Lambda
- GitHub workflow job will run below steps
- Validate the syntax of CloudFormation template
- Static Analysis of the CloudFormation template
- Create CloudFormation Stack
Lets begin in detail on the implementation with CloudFormation and workflow.
CloudFormation resources to create AutoTag EC2 workflow
CloudFormation template is packaged to implement the Autotag EC2 instances workflow, lets look into the each resources which we are creating from the template
-
In below resource, RuleForEC2tagging is the logical ID to create EventBridge rule and source is "aws.ec2" and event name is "RunInstances" and target will be Lambda which we I will be showing up in further
resource section. This is pretty simple, in layman term we are creating an event bridge rule to trigger the lambda whenever an EC2 instance is launched
RuleForEC2tagging:Type: "AWS::Events::Rule"Properties:Name: !Ref EventBridgeRuleNameDescription: "While EC2 instance is launched, This rule will trigger"EventPattern:source:- aws.ec2detail-type:- AWS API Call via CloudTraildetail:eventName:- RunInstancesState: "ENABLED"Targets:- Arn: !GetAtt AutotaggingLambda.ArnId: "TargetFunctionV1"
-
In below resource, PermissionForEventsToInvokeLambda is the logical ID to provide the permission for lambda to invoke a function for EventBridge source. This is mandatory resource when you are creating via
CloudFormation template
PermissionForEventsToInvokeLambda:Type: "AWS::Lambda::Permission"Properties:FunctionName: !GetAtt AutotaggingLambda.ArnAction: "lambda:InvokeFunction"Principal: "events.amazonaws.com"SourceArn: !GetAtt RuleForEC2tagging.Arn
-
In below resource, LambdaRole is the logical ID to create a IAM role for lambda to call the certain API actions. Here, we are using ec2 create tags and describe images API calls in lambda function and
AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole managed policy is required to put the logs to CloudWatch log stream
LambdaRole:Type: 'AWS::IAM::Role'Properties:RoleName: !Ref LambdaRoleNameAssumeRolePolicyDocument:Version: 2012-10-17Statement:- Effect: AllowPrincipal:Service:- lambda.amazonaws.comAction:- 'sts:AssumeRole'Policies:- PolicyName: rootPolicyDocument:Version: 2012-10-17Statement:- Effect: AllowAction:- "ec2:CreateTags"- "ec2:DescribeImages"Resource: "*"ManagedPolicyArns:- arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/service-role/AWSLambdaBasicExecutionRole
-
Final resource is lambda creation part, where AutotaggingLambda is the logical resource to create a lambda function. Function is very simple, where I am getting the RunInstances event from EventBridge
and I am further tagging the launched resource with below provided logic in the lambda handler
AutotaggingLambda:Type: AWS::Lambda::FunctionProperties:FunctionName: !Ref LambdaFunctionNameCode:ZipFile: |import jsonimport boto3def lambda_handler(event, context):try:print(event)items = event["detail"]["responseElements"]["instancesSet"]["items"]region = event["detail"]["awsRegion"]LaunchedBy = event["detail"]['userIdentity']['arn']for item in items:instanceid= item['instanceId']amiid = item['imageId']ec2client = boto3.client('ec2', region_name = region)response= ec2client.describe_images( ImageIds=[amiid])AMI_Name= response['Images'][0]['Name']ec2client.create_tags(Resources=[instanceid,],Tags=[{'Key': 'OS_Name','Value': AMI_Name},{'Key': 'LaunchedBy','Value': LaunchedBy},])except Exception as e:print(e)Description: Custome AMI TaggingHandler: index.lambda_handlerMemorySize: 128Role: !GetAtt LambdaRole.ArnRuntime: python3.7Timeout: 900
Github Workflow to deploy the CloudFormation template using Github Actions
As a pre-requisites, in order to deploy your resources in AWS, you will have to pass the user credential in Github secrets as shown below
Create a programmatical IAM user from AWS console, please refer AWS official doc for the steps to create an IAM user. Add the secret
keys and access secrets keys in GitHub secrets.
-
Lets look into the GitHub workflow. As per below workflow, GitHub actions will automatically execute when you push or create the pull request to main branch
name: 'Deploy to AWS CloudFormation'on:push:branches: [ main ]pull_request:branches: [ main ]
-
actions/checkout@v2 action checks-out your repository under $GITHUB_WORKSPACE, so your workflow can
access it. For more details on checkout action visit GitHub official doc
steps:- name: Checkoutuses: actions/checkout@v2
-
ScottBrenner/cfn-lint-action@1.6.1 GitHub Action used for CloudFormation Linter. More details can be found in GitHub page
- name: cfn-lint-actionuses: ScottBrenner/cfn-lint-action@1.6.1with:args: "cloudformation/**/*.yaml"
-
minchao/cfn-nag-action@v0.1 is cfn-nag tool which looks for patterns in CloudFormation templates that may indicate insecure infrastructure.
- name: cfn-nag-actionuses: minchao/cfn-nag-action@v0.1with:args: "--input-path cloudformation/"
In Layman terms, it will look for:
- IAM rules that are too permissive (wildcards)
- Security group rules that are too permissive (wildcards)
- Access logs that aren't enabled
- Encryption that isn't enabled
- Password literals
-
actions/upload-artifact@v1 uploads artifacts from your workflow allowing you to share data between jobs and store data once a workflow is complete. Here, we are using to keep the artifacts which is CloudFormation in
Github Artifacts. More details can be looked in GitHub page
- name: cfn-artifactsuses: actions/upload-artifact@v1with:name: cloudformation-artifactspath: cloudformation/
-
aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1 is used to configure AWS credential and region environment variables. More details can be looked in
GitHub page
- name: Configure AWS Credentialsuses: aws-actions/configure-aws-credentials@v1with:aws-access-key-id: ${{ secrets.ACCESS_KEY }}aws-secret-access-key: ${{ secrets.ACCESS_KEY_SECRET }}aws-region: ap-south-1
-
aws-actions/aws-cloudformation-github-deploy@v1 is used to deploy the AWS CloudFormation Stacks. More details can be looked in GitHub page
- name: Deploy to AWS CloudFormationuses: aws-actions/aws-cloudformation-github-deploy@v1with:name: ec2-auto-tag-stacktemplate: cloudformation/ec2-auto-tag.yamlno-fail-on-empty-changeset: "1"parameter-overrides: >-LambdaRoleName=ec2TaggingRole,EventBridgeRuleName=ec2TaggingRule,LambdaFunctionName=ec2TaggingFunctionCapabilities: CAPABILITY_NAMED_IAM
You can clone my GitHub repo
and deploy this setup in your environment
Now it's time to test the deployment. Lets push the code to the repo and check the workflow. I pushed the code and created the pull request from feature branch to main branch, my workflow automatically triggered



You can see, workflow triggered and each step executed sequentially one after the other, if syntax is wrong in CloudFormation then cfn-lint-action will fail and trigger an email to you and on the other step if you have given over-permissive in your role then cfn-nag-action step will fail. After validation, we can see
stack executed in the given AWS account and region. you can take this workflow as a reference and build your infrastructure.
Conclusion
In this blog post, I have shown you how to tag your EC2 instances with "OS version" and "Launched By" key with its respective values using Lambda and Event bridge. I also showed you on how the whole design can be packaged in
CloudFormation. Following this, I showed you how to deploy the CloudFormation using Github Action by using steps with cfn-lint, cfn-nag and cfn-deploy. Hope this blog helped you in your similar use case.
Thank you for reading!
Comments
Post a Comment